Please note: a valid prescription is required for all prescription medication.
Hemangiol® Oral Solution for Infantile Hemangioma
$404.99
Secure Encrypted Payments
Hemangiol is a prescription propranolol oral solution for infantile hemangioma. This page explains how it works, who it is for, and safe use. You can review Hemangiol® price without insurance and arrange US delivery from Canada.
YouDrugstore is a licensed Canadian pharmacy in Manitoba. Pharmacists review prescriptions before dispensing.
What Hemangiol Is and How It Works
This medicine contains propranolol, a nonselective beta blocker. It reduces the growth signals that drive hemangioma thickening and color. Over time, lesions often become lighter and flatter. The oral solution is weight-based, so the dose is adjusted to the infant’s current weight.
On-label use targets complicated or proliferating lesions that need systemic therapy. The class can slow heart rate and lower blood pressure. It may reduce tremor-like vessel activity and limit excess blood flow in the lesion. The approved solution is designed for precise pediatric dosing.
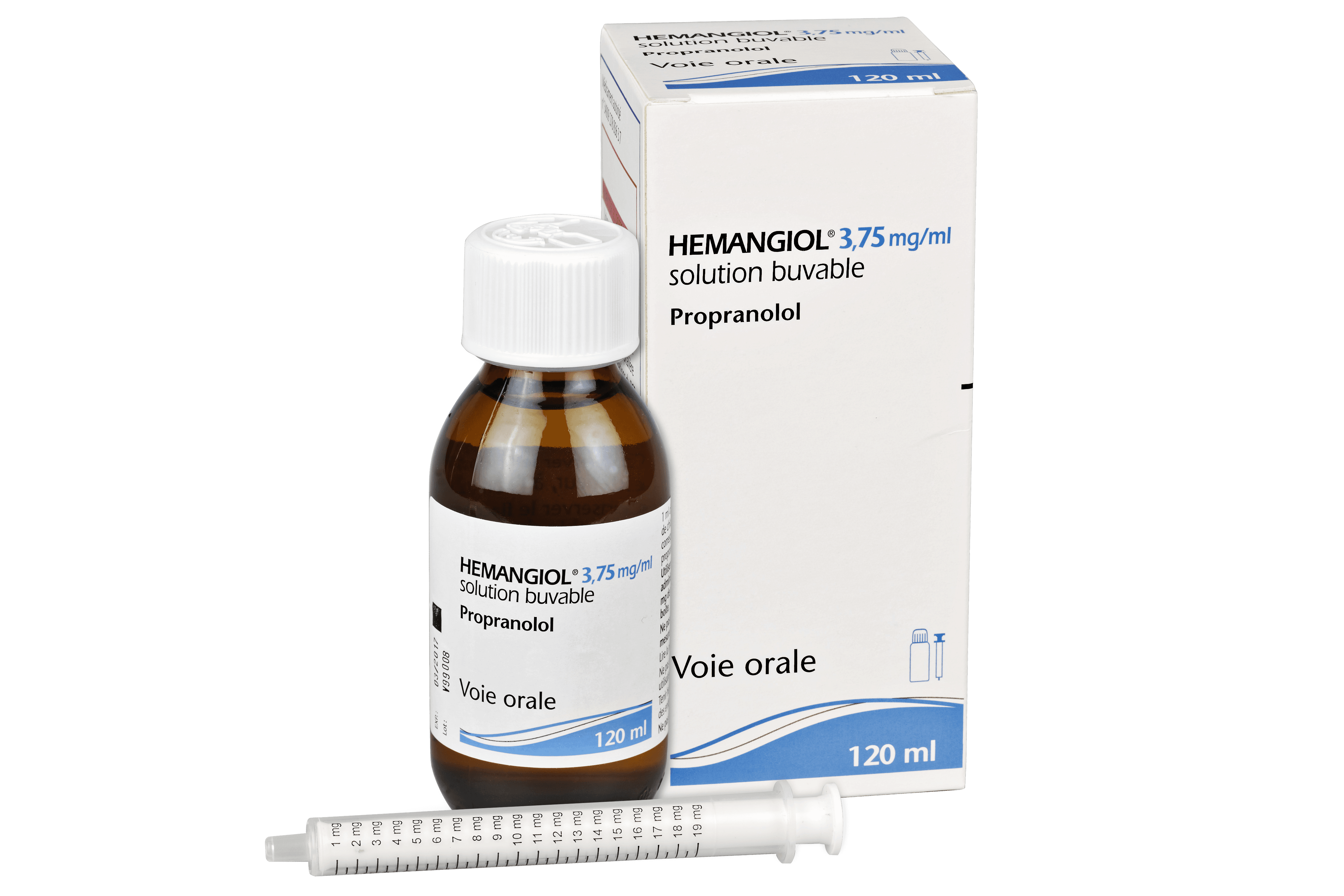
The formulation is a propranolol oral solution 4.28 mg/mL. Give doses during or immediately after a feeding to lower the risk of low blood sugar.
Who It’s For
This treatment is for infants with proliferating infantile hemangioma who need systemic therapy. It is typically started by a pediatric specialist after confirming benefits outweigh risks. Children with small, uncomplicated lesions usually do not need systemic therapy.
It may not be appropriate for infants with asthma or recurrent wheezing, significant heart block, low heart rate, very low blood pressure, or known hypersensitivity to propranolol. Clinicians also assess feeding patterns and overall growth before starting therapy.
Dosage and Usage
Caregivers follow a weight-based schedule set by the prescriber. Doses are typically given twice daily during or soon after feeding. If the label includes a titration plan, follow it as written. The clinician may increase the dose after one or two weeks if tolerated.
Measure each dose with the provided device or a calibrated oral syringe. Never use a kitchen spoon. If the infant is not feeding well, has vomiting, or is ill, contact the prescriber for guidance on holding doses. Keep a simple log of doses, feeds, and any symptoms.
The prescriber will monitor heart rate, blood pressure, and growth at visits. Do not change the dose without medical direction. If instructions differ from this overview, use the official label and your clinician’s plan.
Strengths and Forms
The treatment is supplied as an oral solution in a bottle, commonly dispensed with a dosing device. A frequently referenced presentation is Hemangiol 4.28 mg/mL oral solution. Some markets supply a 120 mL bottle. Availability can vary by region and supplier.
Always check your pack size and the measuring syringe volume before first use. If you receive a different device than expected, ask your pharmacist for help.
Missed Dose and Timing
If a dose is missed, give it when remembered unless it is close to the next scheduled dose. Do not double up. Keep dosing tied to feeds to reduce the chance of low blood sugar. If the infant vomits after a dose, do not repeat; resume at the next scheduled time unless your clinician advises otherwise.
Storage and Travel Basics
Keep the bottle tightly closed and out of children’s reach. Store according to the label. Protect from moisture and keep in the original bottle to retain dosing instructions and lot details. Do not freeze. Avoid leaving the bottle in a hot car or near a heater.
For travel, pack the medicine in your carry-on. Bring the prescription label and a copy of your prescription for security checks. Use a childproof bag or container to prevent accidental ingestion. If you cross time zones, ask your clinician how to keep doses aligned with feeding times.
Benefits
This therapy offers a well-studied approach to shrinking and fading certain infantile hemangiomas. Liquid dosing supports accurate, weight-based administration. Twice-daily dosing pairs with regular feeds. The treatment can reduce the need for invasive procedures in appropriate cases. Caregiver education and monitoring are built into the treatment plan.
Side Effects and Safety
Common effects may include sleep changes, irritability, cold hands or feet, stomach upset, diarrhea, or vomiting. Many are mild and improve with time or dose adjustments under medical supervision.
Serious but less common risks include low blood sugar, significant bradycardia, low blood pressure, wheezing or bronchospasm, and allergic reactions. Seek urgent care for severe breathing trouble, unusual lethargy, a seizure, or poor responsiveness. Hypoglycemia risk increases with prolonged fasting, illness, or reduced feeding; keep feeds regular and follow your clinician’s sick-day plan.
Drug Interactions and Cautions
Tell your healthcare professional about all medicines, including over-the-counter products and supplements. Other blood pressure or heart rate medicines, certain calcium channel blockers, and digoxin may increase bradycardia risk. Some anesthetics and sedatives can amplify cardiovascular effects. CYP2D6 inhibitors may raise propranolol levels.
Use caution with respiratory conditions, congenital heart disease, or metabolic disorders. Do not stop therapy abruptly without medical guidance. Laboratory or clinic monitoring may be needed at intervals.
What to Expect Over Time
Lesions may gradually soften, lighten, and flatten over weeks to months. The prescriber often continues therapy for a defined course, then reassesses. Some infants need longer treatment, while others can stop earlier. After treatment ends, your clinician may watch for signs of regrowth and guide follow-up.
Consistent dosing with feeds supports steadier response and reduces low blood sugar risk. Keep follow-up appointments and record any changes in the lesion’s size or color between visits.
Compare With Alternatives
Clinicians sometimes consider other options when this therapy is not suitable. Oral tablets of propranolol may be used off-label in select cases under specialist care. See our listing for Propranolol. Another beta blocker, Nadolol, may be discussed by specialists for specific scenarios. Choices depend on the child’s condition, comorbidities, and response.
Pricing and Access
You can check current cash-pay figures and see if a manufacturer or pharmacy coupon applies. We offer Canadian pricing with transparent checkout. To compare options and buy propranolol oral solution, sign in and view the product page once your prescription is ready. Encrypted checkout protects your information.
Looking for a deal? See our current offers on the Promotions page. We provide US shipping from Canada for eligible orders. Final amounts can vary by quantity and prescriber directions.
Availability and Substitutions
Supply can vary. If the item is temporarily unavailable, your prescriber may recommend an alternative or a different pack size. If you need cross-checks on formulations, ask our team to coordinate with your clinician. You can also order propranolol solution from Canada when an equivalent, prescriber-approved option is appropriate.
Patient Suitability and Cost-Saving Tips
Good candidates include infants with problematic or at-risk lesions who can maintain regular feeds and attend monitoring visits. Those with uncontrolled wheezing, significant cardiac conduction issues, or poor feeding may not be candidates. Caregivers should learn signs of low blood sugar and when to hold a dose during illness.
To stretch budgets, consider multi-month quantities when clinically appropriate, align refills with follow-up visits, and set reminders. Ask your prescriber if multiple bottles per fill fit the plan. Discuss coverage and expected Hemangiol cost with your pharmacy team before checkout.
Questions to Ask Your Clinician
- Starting dose plan: how dosing will be titrated over time.
- Feeding link: what to do if feeds are delayed or reduced.
- Monitoring: which signs require calling the clinic or urgent care.
- Illness plan: when to hold doses during vomiting or poor intake.
- Duration: expected course length and tapering approach if needed.
- Alternatives: when tablets or another beta blocker might be considered.
- Follow-up: timing for weight checks and dose adjustments.
Authoritative Sources
See official information and professional labels here:
Learn about the condition and related care options across our site. Explore Infantile Hemangioma resources. For broader skin therapies, visit Dermatology. If your clinician recommends another cardiovascular beta blocker, see Atenolol or our hospital-use Propranolol Hcl Injection Vial. For dermatology news, read World Psoriasis Day.
Ready to proceed? Add to cart, upload your prescription, and complete checkout for prompt US shipping from Canada and temperature-controlled handling when required. This content is for general information and does not replace your clinician’s advice.
Express Shipping - from $25.00
Shipping with this method takes 3-5 days
Prices:
- Dry-Packed Products $25.00
- Cold-Packed Products $35.00
Shipping Countries:
- United States (all contiguous states**)
- Worldwide (excludes some countries***)
Standard Shipping - $15.00
Shipping with this method takes 5-10 days
Prices:
- Dry-Packed Products $15.00
- Not available for Cold-Packed products
Shipping Countries:
- United States (all contiguous states**)
- Worldwide (excludes some countries***)
How does this oral solution work for infantile hemangioma?
It contains propranolol, a nonselective beta blocker. By blocking beta-adrenergic receptors, it reduces signals that promote blood vessel growth and dilatation inside the lesion. Over time, this can soften, lighten, and flatten certain hemangiomas that require systemic therapy. Dosing is weight-based and tied to feeds to limit hypoglycemia risk. Your clinician will monitor heart rate, blood pressure, and overall growth during treatment and adjust the plan when needed.
When do clinicians typically start therapy in infants?
Specialists usually start therapy in infants with proliferating or complicated lesions at risk of functional problems, ulceration, or disfigurement. It is often initiated after about 5 weeks of age in appropriate candidates, with careful screening for respiratory or cardiac concerns. The prescriber titrates the dose based on tolerance and weight, then reassesses the need for continuation after a defined course. Always follow the official label and your clinician’s plan.
What are the key safety risks caregivers should watch for?
Watch for wheezing or breathing difficulty, unusual sleepiness, pallor, cold extremities, feeding problems, or signs of low blood sugar like sweating or jitteriness. Seek urgent care for severe breathing trouble, a seizure, or poor responsiveness. Keep feeds regular, avoid prolonged fasting, and contact your clinician if illness or vomiting occurs. Do not change or stop the medicine without medical guidance. Keep all follow-up appointments for monitoring.
How should doses be given if my child is ill or not feeding?
If the infant has reduced intake, vomiting, or an acute illness, notify your prescriber. Doses are typically held during poor feeding to reduce hypoglycemia risk, then restarted when feeds normalize, per medical advice. Give doses during or immediately after a feed. Do not double a missed dose. Keep a simple log of feeds and doses, and ask your clinician for a sick-day plan tailored to your child.
Can this be used with other heart medicines or anesthesia?
Tell your clinician about all medicines and planned procedures. Other heart rate or blood pressure drugs, like certain calcium channel blockers or digoxin, can increase bradycardia or hypotension risk. Some anesthetics and sedatives may amplify cardiovascular effects. If surgery or sedation is scheduled, the medical team may adjust timing or monitoring. Never change doses on your own. Provide a full medication list at every visit.
How long is treatment usually continued?
Many infants receive therapy for several months, with periodic reassessment. If response is adequate and the lesion is stable, clinicians may consider tapering. Some children need longer courses. After discontinuation, your clinician may observe for signs of regrowth. There is no one-size-fits-all timeline, and decisions depend on response, tolerability, and the lesion’s characteristics. Follow the plan on your prescription label and clinic guidance.
Are there alternatives if this solution is not suitable?
Alternatives may include specialist-guided use of oral propranolol tablets or another beta blocker in select cases. Topical therapies can be considered for superficial lesions, depending on location and depth. The choice depends on the infant’s health, lesion features, and risk profile. Discuss benefits and risks of each option with your clinician before making changes. If availability is an issue, your pharmacist can coordinate with the prescriber on substitutions.